Fostering Inclusive Education: Nurturing Academic Success through Best Practices
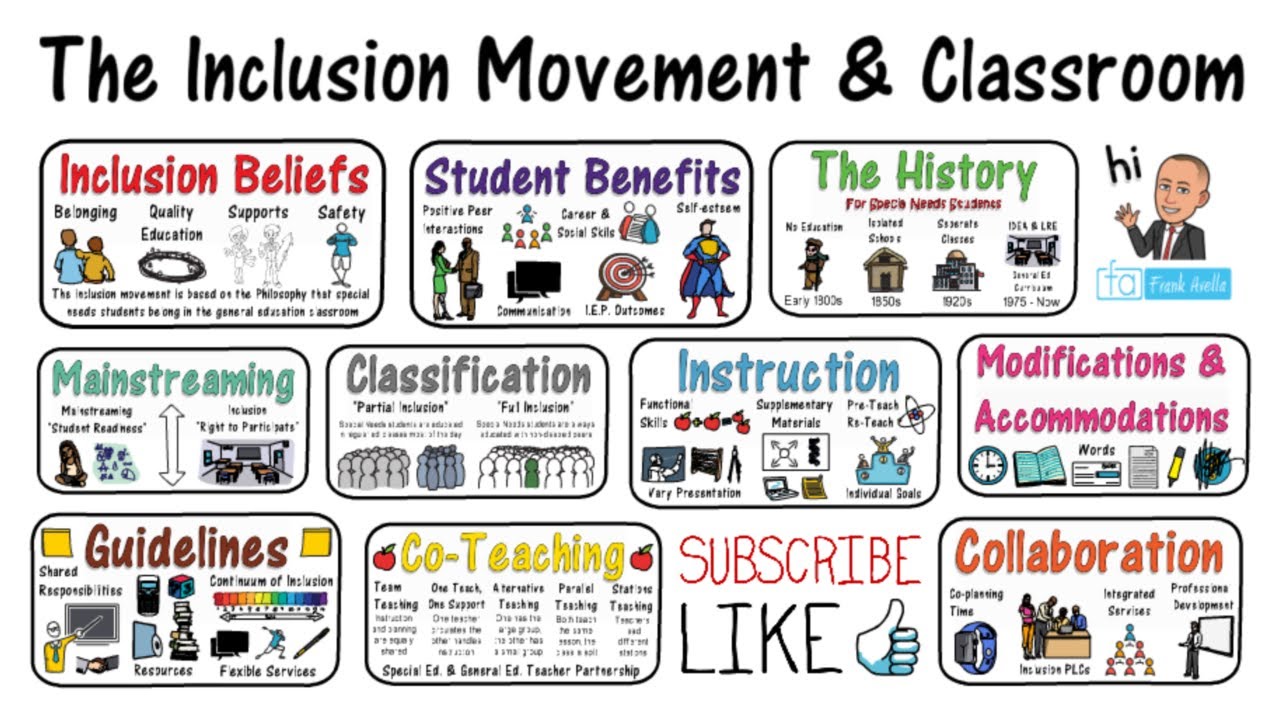
In the pursuit of providing quality education, the focus on inclusive educational practices has gained prominence. These practices aim to create an environment where every learner, regardless of background or ability, feels welcome, supported, and empowered to succeed. Let’s delve into the key components of inclusive education and how they contribute to academic success.
Understanding Inclusive Education
Inclusive education is more than just a buzzword; it’s a philosophy that prioritizes diversity and equity in the educational system. The fundamental principle is to cater to the needs of all learners, including those with disabilities, different learning styles, or diverse cultural backgrounds. It goes beyond mere integration by fostering a sense of belonging and actively involving every student in the learning process.
Creating a Welcoming and Supportive Environment
At the heart of inclusive educational practices is the commitment to creating an environment where every student feels valued and accepted. This involves promoting a culture of respect, understanding, and empathy among students, educators, and staff. By cultivating a sense of belonging, the educational setting becomes a space where diversity is celebrated, and each learner is encouraged to thrive.
Differentiated Instruction for Diverse Learning Needs
One of the key strategies in inclusive education is differentiated instruction. Recognizing that learners have varying needs and abilities, educators tailor their teaching methods and content to accommodate diverse learning styles. This approach ensures that each student can engage with the material in a way that suits their individual strengths and challenges, fostering a more inclusive and effective learning experience.
Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
Universal Design for Learning is a framework that takes inclusivity a step further by proactively designing educational materials and activities to cater to a broad range of learners. It acknowledges that students have different preferences and abilities in how they acquire information and demonstrate understanding. By incorporating multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression, UDL ensures that educational content is accessible to all.
Supporting Students with Special Needs
Inclusive education places a strong emphasis on providing adequate support for students with special needs. This may involve accommodations such as assistive technologies, additional resources, or individualized learning plans. By addressing the unique requirements of each student, educators can ensure that all learners have an equal opportunity to participate and succeed in the educational journey.
Promoting Collaborative Learning Environments
Inclusive education thrives on collaboration and teamwork. Creating opportunities for students to work together, share perspectives, and learn from one another fosters a sense of community. Collaborative learning environments not only enhance academic outcomes but also contribute to the development of social skills, empathy, and a deeper appreciation for diversity.
Continuous Professional Development for Educators
Educators play a crucial role in implementing inclusive educational practices. Continuous professional development is essential for equipping teachers with the knowledge, skills, and strategies needed to create an inclusive classroom. This may involve training on diverse teaching methods, cultural competency, and understanding various learning disabilities. The ongoing growth of educators directly translates into a more inclusive and effective learning experience for students.
Family and Community Involvement
Inclusive education extends beyond the classroom walls to involve families and the broader community. Collaborating with parents, guardians, and community members ensures a holistic approach to supporting the diverse needs of learners. Open communication channels and partnerships between schools and the community contribute to a more comprehensive and inclusive educational experience.
Assessment and Evaluation for Fairness
Inclusive educational practices extend to the assessment and evaluation process. Ensuring fairness in how students are assessed involves considering diverse ways of demonstrating understanding and skills. This may include alternative forms of assessment, extended time for exams, or the use of varied evaluation methods that accommodate different learning styles.
Fostering a Culture of Lifelong Learning
Inclusive education goes hand in hand with the cultivation of a culture of lifelong learning. Encouraging students to embrace learning as a continuous journey promotes resilience, adaptability, and a positive attitude towards diversity. In this way, inclusive educational practices contribute not only to academic success but also to the holistic development of individuals prepared for the challenges of a diverse and dynamic world.
For comprehensive insights into inclusive educational practices, explore Inclusive Educational Practices.
